The way software is built has fundamentally changed in the last few years. Artificial Intelligence has moved from being an experimental tool to a daily companion for developers around the world. GitHub Copilot, Tabnine, ChatGPT-based assistants, and dozens of other platforms are now integrated into IDEs, cloud environments, and DevOps pipelines. They write functions, generate tests, autocomplete configuration files, and even provide architectural recommendations. By 2025, the adoption curve is no longer in question: AI-powered code generation is here to stay. But the key question for businesses and engineers is different — can AI-generated code truly be trusted in production, where reliability, security, and maintainability are critical?
Software development team leads and engineering managers.
Startups building MVPs and scaling SaaS products.
Developers interested in AI-powered productivity tools.
- AI-powered code generation boosts productivity, but it is not a replacement for engineers.
- Treat AI as a super-fast junior developer: great at boilerplate and prototyping, but always in need of human supervision.
- The future of software development is hybrid teams where AI augments human creativity and decision-making.
The Promise of AI-Powered Code
The appeal of AI-assisted coding is obvious. It allows companies to move faster, reduce costs, and empower teams. Startups that once needed half a year to deliver a minimum viable product can now get prototypes into the hands of investors and early customers in less than three months. Enterprise development teams report that AI handles much of the boilerplate, from CRUD operations to API integrations, leaving human engineers free to concentrate on complex business logic and scalability challenges.
Developers themselves experience the shift firsthand. Junior engineers are using AI as an interactive tutor, learning better practices through suggested completions. Senior engineers leverage it as a brainstorming partner that accelerates prototyping. The result is not replacement, but augmentation: human creativity multiplied by machine speed.
The Risks Beneath the Surface
However, the advantages of AI come with significant risks when code leaves the prototype stage and enters production. Security remains the most pressing concern. AI tools are trained on massive datasets that may contain vulnerable or outdated code. As a result, they sometimes reproduce unsafe patterns or suggest dependencies with known vulnerabilities. Studies in 2024 revealed that nearly half of AI-generated code snippets contained at least one security flaw.

Beyond security, there is the problem of maintainability. AI-generated code can appear correct but lack consistency, clarity, or alignment with project standards. Over time, unreviewed AI contributions accumulate as technical debt, slowing down development rather than speeding it up. Intellectual property questions also persist. If models were trained on copyrighted repositories, can businesses safely use the output without legal exposure? In 2025, this debate is still ongoing, with lawsuits shaping how companies approach AI tools.
Lessons from Real-World Adoption
Despite the risks, adoption continues to grow. Enterprises are experimenting with embedding AI not only in the development stage but also directly into CI/CD pipelines. For example, some teams now rely on AI to generate regression tests every time a feature is merged. Startups, on the other hand, use AI to validate product concepts quickly, even if they later replace the generated code with production-ready rewrites.
Case studies show a mixed but promising picture. A SaaS company in Europe reduced time-to-market for a new product release by 38% thanks to AI-powered development, but they also tripled their QA budget to ensure the generated code met security and performance standards. This balance — speed offset by rigorous testing — is the formula that is proving most effective in 2025.
Can We Trust AI in Production?
The answer is not black and white. AI-generated code can be used in production, but only with the right safeguards. Businesses must treat AI as an extremely fast but inexperienced junior developer. It produces output at lightning speed, but everything must be verified by human engineers. Organizations that succeed with AI in production environments establish strict review policies, integrate automated testing, and enforce continuous monitoring. Without these controls, using AI blindly is equivalent to gambling with the stability of the product.
Discover how to use AI as a co-pilot, not an autopilot!
Contact UsBest Practices Emerging in 2025
The most mature organizations using AI-powered code generation follow a clear set of practices. First, all AI-generated contributions go through human-in-the-loop code review. Nothing is merged directly without oversight. Second, automated pipelines — linting, unit tests, integration tests, and vulnerability scans — are mandatory for every commit. Third, AI is applied selectively: it handles boilerplate, test generation, and routine refactoring, while humans remain responsible for core business logic, payments, or security-sensitive modules. Finally, companies invest in educating developers about AI literacy. Engineers must know when to trust AI suggestions and when to challenge them.
The Future Outlook
By 2025, the industry has largely accepted that AI-powered coding tools are not a temporary trend but a permanent part of the developer’s toolkit. Gartner estimates that nearly three-quarters of enterprises already integrate AI into their software development lifecycle, and analysts project the market for coding assistants will surpass 12 billion dollars by 2026.
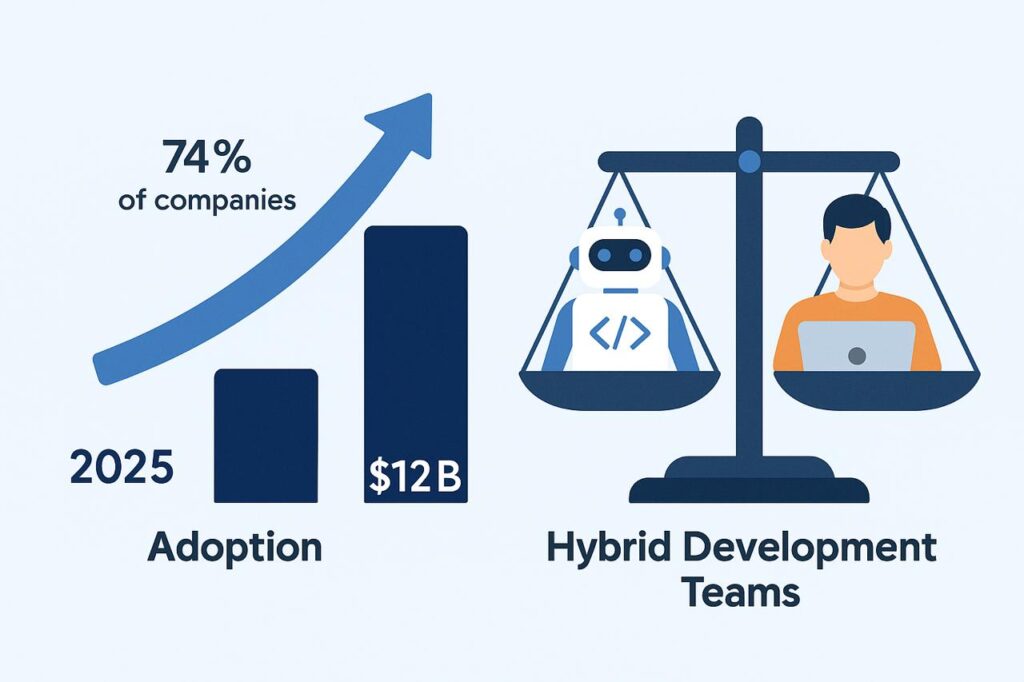
Yet the prevailing sentiment among engineering leaders is cautious optimism: AI is a force multiplier, but it is not ready to replace human judgment. The future of software development looks hybrid, with AI augmenting teams that remain firmly human-led.
Conclusion
AI-powered code generation in 2025 represents both an extraordinary opportunity and a significant responsibility. It allows businesses to innovate faster, deliver products more efficiently, and empower developers at every level. But trust in production comes only with discipline. Human oversight, strong security practices, and clear policies remain essential. The organizations that thrive will not be those that hand control over to AI completely, but those that use it as a co-pilot — accelerating their journey without losing control of the wheel.
In 2025, AI should not be your autopilot. It should be your co-pilot — a partner that helps you move faster, but never replaces the expertise and accountability of a skilled human team.
Why Ficus Technologies?
In a world where every business is exploring AI-powered solutions, what makes Ficus Technologies the right partner to trust? The answer lies in our combination of technical expertise, business vision, and hands-on experience delivering scalable, secure, and innovative products.
At Ficus, we don’t just experiment with new technologies — we turn them into reliable tools that drive business growth. Our engineers have deep expertise in AI/ML development, cloud solutions, and modern software architectures, ensuring that every project we deliver is not only fast to market but also built to last.
We understand that trust in production requires more than just writing code.
That’s why our approach combines:
- Rigorous security standards aligned with global regulations and best practices.
- Agile development processes that keep stakeholders aligned and projects on track.
- Custom-tailored solutions instead of one-size-fits-all tools, ensuring our clients’ unique needs are always at the center.
- Long-term partnership rather than short-term outsourcing, helping businesses grow and scale sustainably.
By working with Ficus Technologies, companies gain not only access to cutting-edge expertise but also a strategic partner who understands how technology supports business objectives. For us, AI-powered code generation, cloud transformation, and digital innovation are not buzzwords — they are everyday practice.
AI-powered code generation uses large language models (LLMs) trained on vast datasets of code to suggest or create new code. These tools can automate repetitive tasks like boilerplate, tests, and simple logic, helping developers work faster.
Yes, but only with safeguards. AI-generated code should be reviewed by senior developers, tested automatically through CI/CD pipelines, and scanned for vulnerabilities before deployment.
The biggest risks are security flaws, lack of maintainability, potential copyright/IP issues, and over-reliance on AI suggestions. Without human oversight, these risks can harm production systems.